America’s farmers and ranchers are leading the way in greenhouse gas emission reduction through voluntary conservation efforts and market-based incentives.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released the Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2022. The report shows American agriculture reduced emissions by almost 2% from 2021 to 2022, the largest decrease of any economic sector.
“U.S. agriculture represents just under 10% of total U.S. emissions when compared to other economic sectors,” American Farm Bureau Federation (AFBF) economists said in a Market Intel report. “By EPA’s own methodology, emissions from agriculture totaled 634 million metric tons in CO2 equivalents, or 9.99% of all U.S. emissions, during 2022. This represents a decrease of 1.8%, or 12 million metric tons, from 2021… 2022 marks the lowest U.S. agricultural greenhouse gas emissions since 2012.”
For livestock categories specifically, enteric emissions from beef cattle sat at 2.19% of total U.S. emissions in 2022, or 137 million metric tons of the 6.34 billion metric ton total. This is a 2.43%, or 3.3-million-metric-ton, decline from 2021.
Dairy cattle contributed only 0.77% of total emissions or 49 million metric tons—a 451,000-metric-ton decrease from 2021.
Swine, sheep and horses represented 0.05%, 0.02% and 0.02% of the total, respectively.
Agricultural soil management represents about 50% of all agricultural emissions but only 4.6% of total U.S. emissions.
“The latest numbers demonstrate farmers’ and ranchers’ commitment to growing the food and fiber America’s families rely on while improving the land, air and water, a benefit to the farm and the climate,” AFBF President Zippy Duvall said. “The drop in agricultural emissions highlights the success and importance of voluntary and market-based programs that support farmer efforts in sustainable agriculture practices. The latest numbers should also serve as inspiration to lawmakers who can build on this progress by passing a farm bill, which not only provides a safety net for farmers, but also helps them meet sustainability goals.”
Other highlights specific to the agricultural sector include:
- 12-million-metric-ton reduction in GHG emissions;
- 1% reduction in livestock GHG emissions;
- 7% reduction in crop cultivation emissions; and
- 2% reduction in fuel combustion emissions.
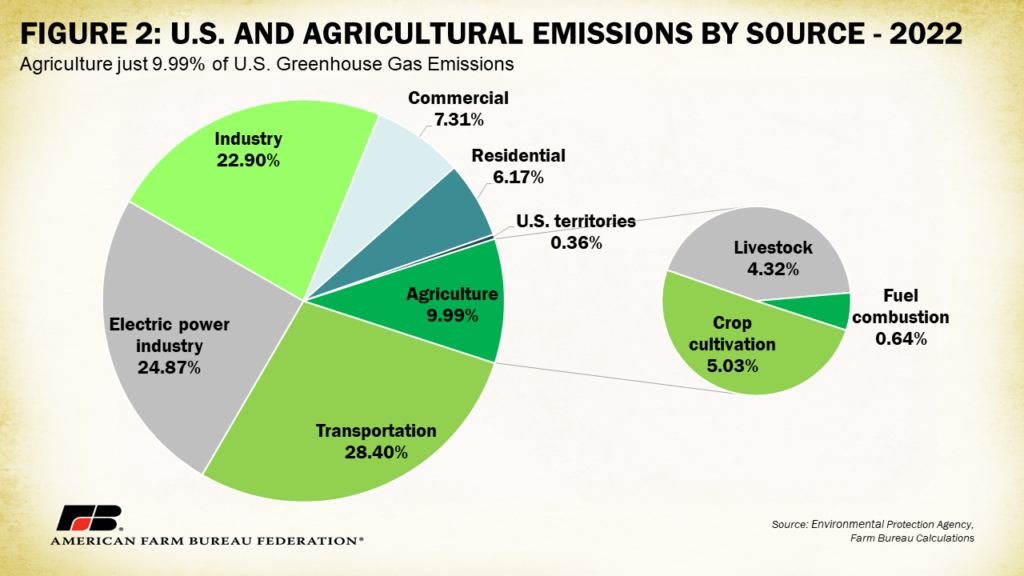
The largest emissions source was the transportation sector, representing 28.4% of total emissions and totaling 1.8 billion metric tons.
Following transportation, electricity generation represented 24.87% of total emissions at 1.57 billion metric tons.
The industrial sector, which includes the production of iron and steel, as well as other input materials like cement, represented 22.9% of all emissions at 1.45 billion metric tons.
The commercial and residential sectors and U.S. territories represented 14% of all U.S. emissions. This category’s emissions are heavily linked to building-related activities such as heating, cooling and cooking.


Leave A Comment